 Communication systems are essential for offices worldwide. Whether it’s a large corporation or a small business, having an internal phone network is vital. The arrival of PABX – the Private Automatic Branch Exchange method – has changed everything.
Communication systems are essential for offices worldwide. Whether it’s a large corporation or a small business, having an internal phone network is vital. The arrival of PABX – the Private Automatic Branch Exchange method – has changed everything.
In the past, landline phones were the primary means of business communication, but they had limitations such as power outages and high costs from service providers. Most business communications capabilities are made possible by implementing private branch exchange (or PBX) systems, but they require operators to manage calls manually.
PABX system not only significantly reduces communication costs for businesses but also enhances the interconnectedness of systems and response times. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between PBX and PABX and how you can implement these solutions in your business.
Jump to ↓
- What Is Private Automatic Branch Exchange?
- How does it differ from PBX?
- How Exactly Does a PABX System Work?
- Benefits of Using PABX Systems
- PABX: Most Important Features
What is PABX and what does it stand for?
We’ve already established that PABX stands for Private Automatic Branch Exchange. It is like a mini-telephone network within a company or organization.
Imagine you have a big office with many employees, and everyone needs to make calls to each other and to people outside the office. Instead of each person having a direct line to the outside world, everyone is connected to a central system—the PABX.
Before PABX came along, businesses had to use human operators to connect calls by hand. This process was time-consuming and lacked efficiency. PABX systems made this whole process automatic.
- Private: This means it’s a system that is used by a specific group or organization, and not available to the public.
- Automated: The system is computer-controlled, which means it can handle tasks like routing calls without the need for a human operator.
- Branch Exchange: This is a term that comes from the days of manual telephone exchanges. In modern terms, it refers to the central point where calls are managed and distributed within the organization.
Originally, PABX systems were connected to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). This meant that all outgoing calls were routed through traditional telephone lines, which were managed by telecom companies. Over time, as technology evolved, many PABX systems started transitioning to Session Initiation Protocol (SIP).
PABX vs. PBX: What’s the Difference?
Nowadays, the terms Private Branch Exchange (PBX) and Private Automatic Branch Exchange (PABX) are used almost interchangeably. This is because in essence, they serve similar fundamental purposes, but the automation and advanced features of PABX systems represent a significant evolution from the older, manual PBX systems.
Initially, PBX telephone systems were manually operated, requiring human operators to connect calls. With technological advancements, PABX systems emerged, automating the call routing process and adding more sophisticated features. Today, many PABX systems have transitioned to IP-PBX, which uses internet protocols for communication, offering even more flexibility and cost savings.
Summary of Differences
- Manual vs. Automatic: Traditional PBX systems require manual operation, while PABX systems automate call routing and management.
- Features and Complexity: PABX systems typically offer more advanced features and capabilities compared to traditional PBX systems.
- Technology Integration: PABX systems are more likely to integrate with modern digital communication technologies.
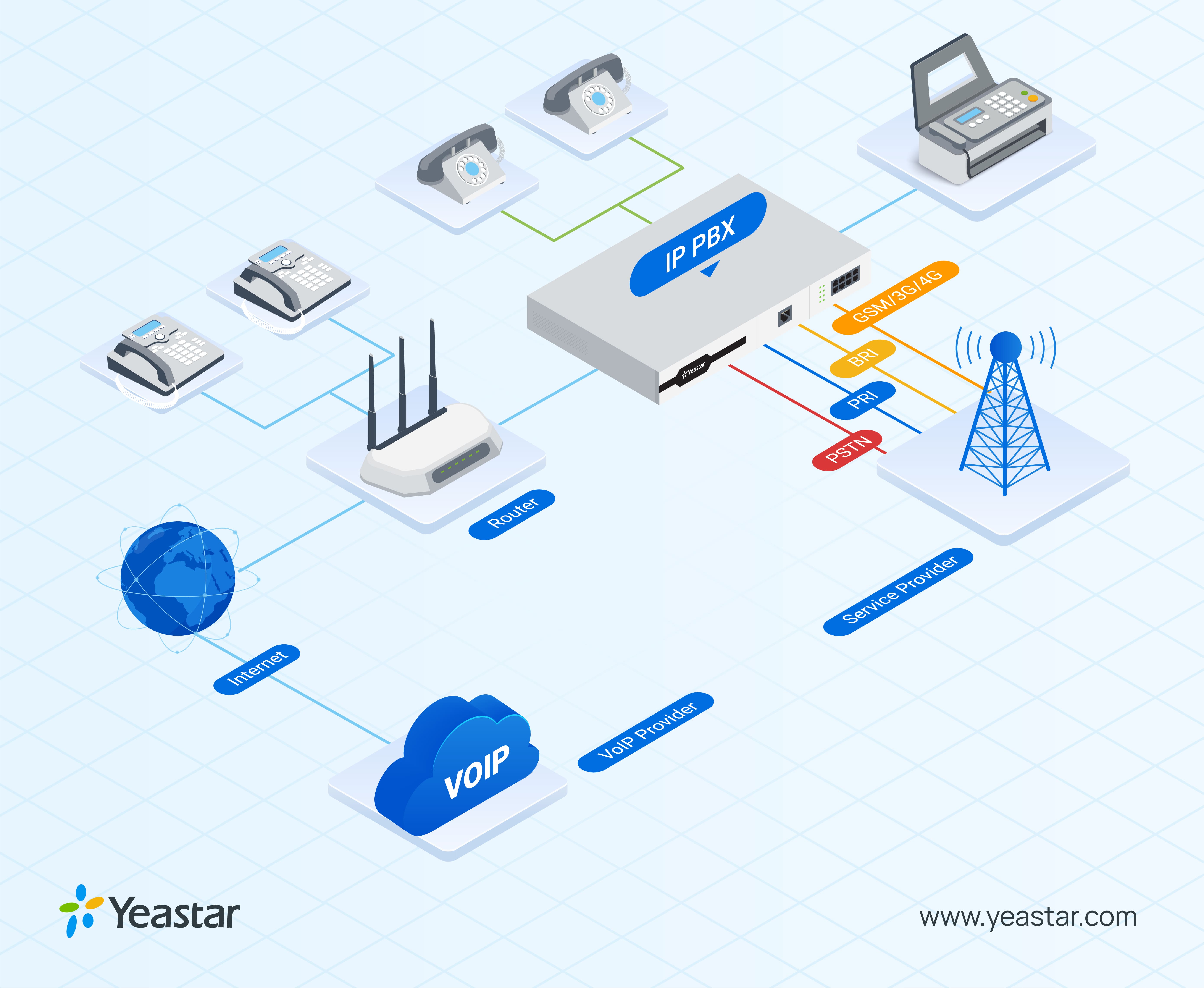
How Exactly Does a PABX System Work?
Private Automatic Branch Exchange (PABX) was made possible by the arrival of the capability to electronically switch between calls without the need for manual operators. This advancement was the key to developing a phone system that would completely do away with the need for hiring people to do the menial task of answering and transferring incoming calls.
Without getting too much into the technicalities, PABX systems, in their most basic version, make use of extension numbers, which are assigned to each VoIP phone and analog phone in a given office. For example, if you’d like to make a call to one of your co-workers who’s in his office next door, the only thing you’d have to do was type in the extension number on your PABX-enabled phone, and the call would directly go through to the receiver.
Private Automatic Branch Exchange (PABX) systems have fixed that by removing the middlemen (operators) while keeping the structure of PBX systems intact. Phone extension numbers remained, but the switchboard was replaced with buttons placed directly on the telephones themselves, allowing any employee to carry out internal phone calls without waiting in line for what sometimes felt like an eternity. Modern PABX systems make use of IP-based phones, and companies providing these services often base their entire functionality around internet connection, removing the need for installing phone lines altogether.
Evolution of PABX System
Private Automatic Branch Exchange (PABX) systems have undergone significant transformations since their inception, evolving from manual switchboard operations to sophisticated digital and cloud-based solutions. This evolution reflects advancements in telecommunications technology and changing business communication needs.
Early Beginnings: Analog PBX Systems
PBX systems started in the late 1800s when businesses used manual switchboards to handle internal calls. They relied on analog signals and copper wires to link phones to a central unit. Early PBX systems were big, costly, and needed operators to manually connect calls. Because of their high cost, only large organizations could afford to install and maintain them.
Transition to Automation: The Rise of PABX
By the 1960s, the need for more efficient communication led to the development of Private Automatic Branch Exchanges (PABX). These systems automated the call routing process, eliminating the need for human operators. Early PABX systems allowed businesses to place internal calls without occupying external phone lines, significantly reducing communication costs and increasing efficiency.
Technological Advancements: From Analog to Digital
The 1970s marked a pivotal shift with the introduction of digital PABX systems. Unlike their analog predecessors, digital systems utilized digital signals, enabling better call quality, more extensions, and advanced features such as call routing and voicemail. This transition also made it easier for businesses to scale their communication systems as needed.
The VoIP Revolution: Cloud-Based PABX
The advent of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) in the late 1990s further transformed PABX technology. Cloud-based PABX solutions emerged, allowing businesses to operate without extensive on-premise hardware. These modern systems leverage internet protocols for voice communication, enabling limitless scalability and integration with various multimedia applications.
Summary of The Evolution:
| Era | Key Features | Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
| Manual PBX | Manual call routing by operators | Analog switchboards |
| Early PABX | Automated internal calling | Early electronic switches |
| Digital PABX | Enhanced call quality, advanced routing | Digital signals |
| Cloud-based PABX | Scalability, multimedia communication | VoIP and internet protocols |
Benefits of Using PABX Systems
- Cost Efficiency: PABX systems reduce call and operational costs through automation and VoIP technology, making communication more affordable for businesses.
- Scalability: Easily expandable, PABX systems allow businesses to add or remove lines and extensions as needed, supporting growth and changing requirements.
- Advanced Features: PABX offers features like auto-attendant, call routing, conference calling, and voicemail, enhancing communication and customer service.
- Improved Productivity: Integration with CRM and unified communications streamlines workflows, enhancing overall productivity and efficiency within the organization
- Centralized Control: PABX systems provide a centralized point of control for managing all telecommunication activities, making it easier to oversee and adjust settings as needed.
PABX: Most Important Features
In our increasingly interconnected and interdependent world, the need for fast, reliable connectivity should be prioritized above anything else. This is especially important in business environments, where minutes (or even seconds) of hesitation or lengthy session initiation can end up costing thousands of dollars.
An increasing number of companies have been utilizing voice over IP (internet protocol) technology to achieve the best results possible. Small businesses are especially looking for cost-effective digital voice solutions. It may be difficult to decide on the right communication service for your business without understanding its main features.
Some of the main characteristics include:
- Effortless call transferring
- Constant connectivity independent from any phone service provider
- Using VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) for the best call quality possible
- Adjustable to the needs of your business
Some advanced features include:
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
- Auto Attendant
- Call Recording
- Conference Call
- Voicemail
- Call waiting
- Call Center
- See All Features Yeastar Support
How To Choose the Right PABX Systems
When selecting a Private Automatic Branch Exchange system, several key considerations must be taken into account to ensure it meets your business needs effectively. Here are the primary factors to consider:
- Business Requirements: This involves understanding your current size, the number of employees, and anticipated growth, ensuring the system you choose can scale accordingly. Additionally, estimating the average daily call volume will help determine the necessary capacity.
- Features and Functionality: Essential features include call forwarding, voicemail, call waiting, and caller ID. Advanced features such as auto-attendant, call recording, conferencing, and CRM integration can significantly enhance business operations. Ensure the system supports remote and mobile workers and is scalable to accommodate future growth.
- Budget and Cost: Evaluate the initial costs, including hardware, installation, and setup fees, as well as ongoing costs such as maintenance, upgrades, and monthly service charges. Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to ensure the investment is justified by the anticipated benefits and efficiencies.
- Reliability and Support: Research the reputation of potential vendors for reliability and customer service. Ensure that 24/7 technical support is available with quick response times, and understand the warranty and service level agreements (SLAs) to ensure comprehensive coverage for repairs and maintenance.
- Security: Ensure the PABX system has robust data protection measures to guard against breaches. Additionally, check for disaster recovery options and data backup solutions to safeguard your business communications in case of emergencies.
- User-friendliness: The system should have an intuitive interface that is easy for both administrators and employees to use. Ensure that training materials and resources are readily available to help users get up to speed quickly and efficiently.
Yeastar Solutions for Your Unified Communication Needs
Private automatic branch exchange (PABX) systems, just like any other product or service, come in all sorts of shapes and sizes. Not all of them will perfectly align with your business needs.
Yeastar solutions are incredibly versatile, making our PABX offer one of the broadest ones in the industry. You can choose between an on-premises VoIP PBX system, granting you the ultimate and complete control over the unified communications at your office. If you want an easy option, our cloud-based PBX system is great for businesses of any size. It offers a reliable UC service without the need for equipment maintenance.
Choose Yeastar for unified communications to improve and maintain seamless connectivity in your office. Regardless of the service you select. This choice will benefit your office for a long time.



Hi we need install PABX and IP PBX
Hi JL, thank you for trust. You can click here to submit your enquiry or send mail to this address sales@yeastar.com. Our sales team will reply you asap.
Do you have branch that sells here in Makati City? Thank you.
Hi Melody, Thank you for your enquiry, you can click here to find our Malaysian distributor Netregy Systems Sdn Bhd. For more information, you can directly mail to sales@yeastar.com and our sales manager will help asap.
We wish to setup a system here in Dubai & back Office in Pakistan, there’ll be around 2-3 personnel in Pakistan & require to contact with customer for Inbound & Outbound however Number of UAE should be appeared in Customer Phones
Hi Muhammad, our sales is on the way to support.
we want to install PABX and 60 phone in our office in Abuja, Nigeria. Do you have any authorized dealer in Abuja.
Hi Sunil, Wavesat Telecommunications Limited is one of our distributors. You can contact them through following methods: phone +234-700-9283728, mail to sales@wavesat.net, or visit the site: https://wavesat.net/product-category/ip-pbx/yeastar-ip-pbx/. For more information, you can click here or mail to our sales: sales@yeastar.com
Did u have branch in Malaysia?
Hi Mohd, you can click here to find our distributors in Malaysia.